Best Practices for Chemical Waste Management in Metal Plating Facilities

July 25, 2025
July 25, 2025
In the metal-plating industry, chemical-waste management is more than a regulatory checkbox—it’s a cornerstone of sustainable, efficient operations. As innovators in metal-finishing chemistry, we’re committed to helping facilities turn compliance into competitive advantage. Below, you’ll find an updated, field-tested roadmap that blends proven tactics with fresh insights.
1. Know your waste stream
Metal plating operations generate a wide range of hazardous waste types, each with its own risks and handling requirements:
Heavy metals such as hexavalent chromium, nickel, cadmium, and zinc are toxic and bioaccumulative, requiring strict control.
Complexed metals from chelated solutions (e.g., nickel or copper complex baths) are difficult to treat and may resist standard precipitation methods.
Cyanide-bearing solutions, often used in copper or silver strike baths, present high acute toxicity and can release dangerous gases during treatment.
Acidic or alkaline rinse waters, generated from pickling or cleaning processes, exhibit extreme pH values and are highly corrosive.
Organic solvents and additives, including degreasers and brighteners, may be flammable or volatile, requiring controlled storage and disposal.
Sludges and spent filters, such as filter press cake and exhausted ion exchange resins, concentrate hazardous components and can be costly to manage.
Proper identification and segregation of these waste types are essential to ensure safe handling, regulatory compliance, and cost-effective disposal.
2. Source reduction starts with smarter Pre-Treatment
The first opportunity to reduce waste is in the surface preparation stage. PAVCO’s Clean-R™, PavPrep™, and PavHib™ product lines help optimize this phase by minimizing contaminants before they enter plating baths.
High-efficiency cleaners like Clean-R™ remove oils and particulates with low-foam surfactants that rinse off easily, reducing the organic load in downstream tanks.
Buffered acid activators such as PavPrep™ LF reduce the aggressiveness of acid attack while maintaining pickling performance. This lowers acid consumption and generates fewer corrosive vapors.
Inhibitors like PavHib™ prevent over-etching and reduce hydrogen absorption in high-strength steels, minimizing the risk of hydrogen embrittlement and decreasing sludge generation from over-treatment.
By optimizing the cleaning and activation stage, you extend the lifespan of your plating baths and cut down on the frequency of bath replacements.
3. Improve Bath Efficiency to Reduce Plating Waste
PAVCO’s plating chemistries are engineered to deliver high performance while minimizing waste. For example:
Niclipse C provides exceptional corrosion protection with lower metal concentrations and better current efficiency. It allows for more uniform deposit thickness, reducing metal drag-out and the need for reprocessing.
These advanced systems often eliminate the need for cadmium and other legacy metals, helping facilities transition away from high-toxicity waste streams.
Their stable formulations extend bath life and reduce frequency of corrective additions, cutting down on the generation of spent baths and treatment sludge.
Choosing efficient, alloy-based plating solutions is one of the most impactful ways to reduce chemical waste and improve process sustainability.
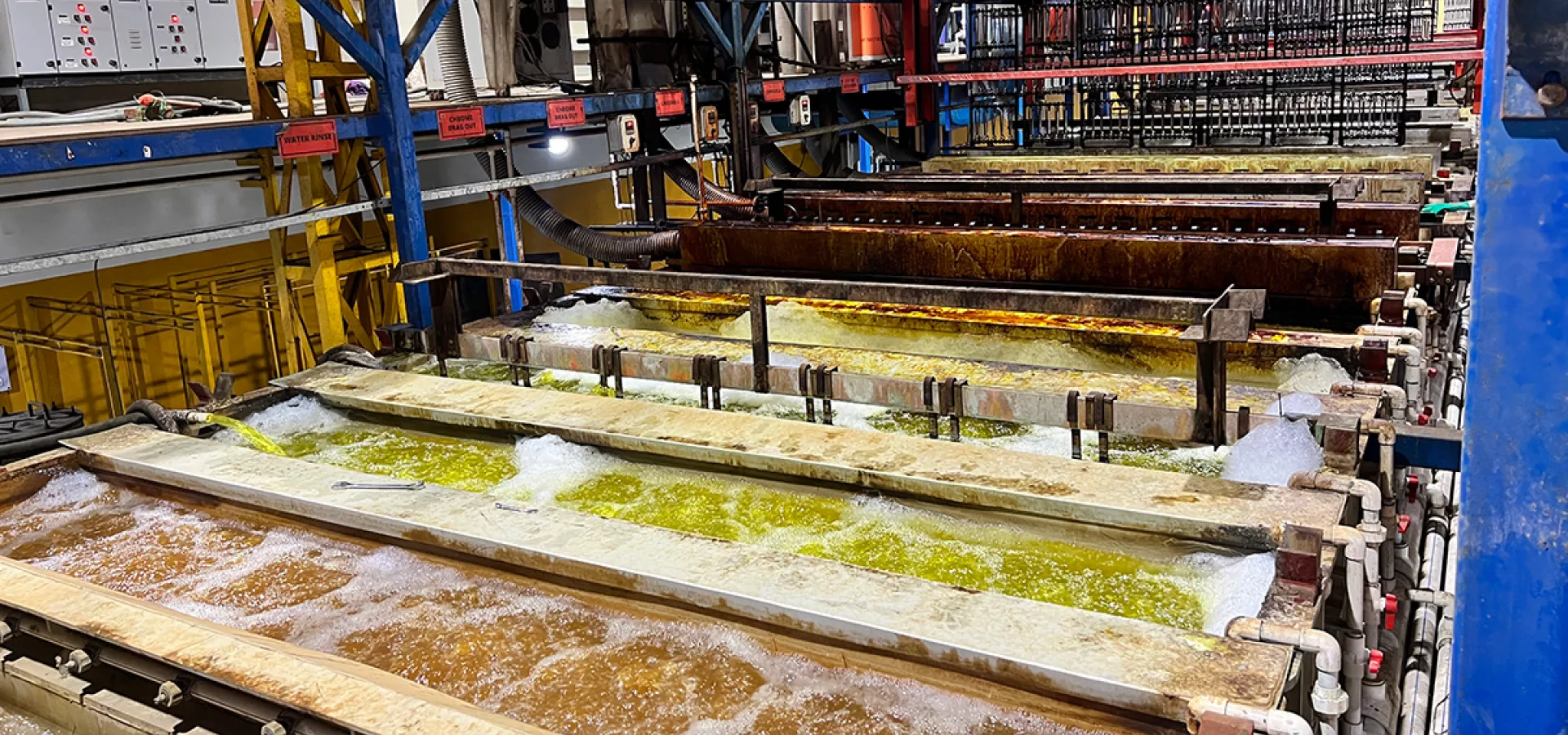
4. Post-Treatment with Sustainability in Mind

Traditional post-plating treatments such as chromates and topcoats often contain hexavalent chromium or volatile organic compounds (VOCs). PAVCO’s post-treatment portfolio is designed to meet modern environmental and performance standards.
Trivalent chromium passivates, such as HyProBlue™ or HyProTec™, offer equal or better corrosion protection compared to hexavalent systems and are REACH-compliant.
Topcoats like HyProCoat™ provide enhanced corrosion resistance, reduced coefficient of friction, and compatibility with automated dosing systems. They extend part life without contributing to air or water pollution.
5. Build a comprehensive Waste-Management Plan
A written plan is the backbone of any successful program. At a minimum, include:
Waste-generation mapping – document every bath, rinse, and maintenance operation.
Treatment & segregation SOPs – specify when to neutralize, precipitate, filter, or separate cyanide streams.
Recycle & recovery loops – detail closed-loop rinses, ion-exchange regeneration, and metal reclamation.
Storage & disposal procedures – align with law’s requirements and local ordinances.
Worker safety & training – cover PPE, spill response, and lock-out/tag-out for treatment units.
Waste Management as a Competitive Advantage
At PAVCO, we don’t just help you treat chemical waste—we help you avoid it through smarter chemistry and better process design. Our portfolio of pre-plate, plating, and post-plate technologies is built around the principle of source reduction, environmental compliance, and operational excellence.
By incorporating our systems into your plating line, your facility can:
Reduce hazardous waste generation at every stage
Extend bath life and reduce chemical consumption
Lower treatment costs and minimize regulatory risks
Position your company as a leader in sustainable surface finishing
Ready to take your waste management strategy to the next level? Reach out to a PAVCO specialist todayto explore customized solutions that improve both your environmental footprint and your bottom line.
IT’S HOW YOU FINISH

We’re a developer and supplier of chemistries for the metal finishing industry since 1948.
In PAVCO, we develop products and deliver services of the highest quality at a reasonable cost.